Not all LEDs are the same!
When selecting the right LED for the development and production of a powerful and long-lasting plant light, there are many points and selection criteria to consider. Even if most LED look the same at first glance, there are big differences in the details.
LED classification
A general distinction is made between the following LED technologies:
High Power LED
- typ. Operating current 350mA and more
- Power 1W to 5W
- 1 chip with to 2mm2
Chip Scale Package LED
- typ. Operating current 350mA and more
- Power 1W to 5W
- 1 chip with to 2mm2
Mid Power LED
- typ. Operating current 350mA and more
- Power 1W to 5W
- 1 chip with to 2mm2
Chip on Board LED (COB)
- typ. Operating current depending on size and internal wiring of the COB
- Power 5W to 100W
- multiple LED chips with up to 0.64mm2 area per chip
Chip Array LED (CA)
- typ. Operating current depending on size and internal wiring of the CA
- Power 1W to 5W
- up to 6 chips with up to 0.64mm2 area per chip

High Power LED and Chip Scale Package LED
High Power LED
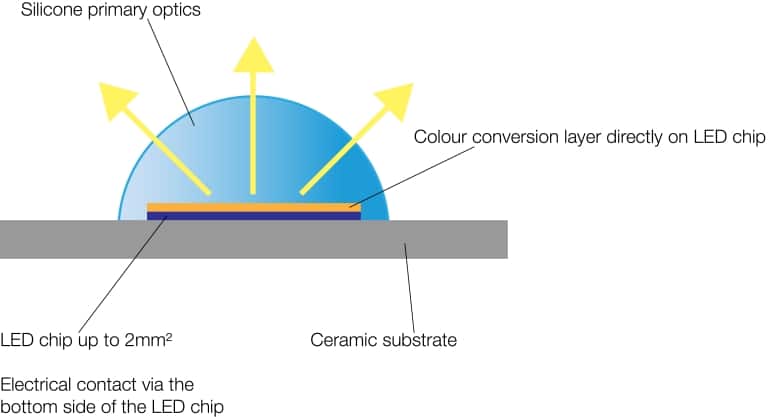
High Power LED are characterized by a high power density. This means that a 3mm x 3mm LED can emit up to 6.2µmol/s of light at an operating current of 700mA. The ultra-thin LED chip is typically mounted on a ceramic substrate and then encapsulated with a primary optic made of silicone. In today’s best high power LED, no reflectors or bond wires are incorporated into the LED. This makes these LEDs extremely robust against external influences such as sulfur, moisture and varying temperatures.
Advantages High Power LED
- Best efficiency with red LED
- up to 4,4µmol/J
- up to 79% Wirkungsgrad
- Extremely robust and durable
- LM90 > 100.000h
Disadvantages from High Power LED
- Cost intensive
- Only medium efficiency with white LED
Chip Scale Package
Basically, chip scale LED are the same as high power LED. However, significantly smaller packages are used. Primary optics are usually dispensed with. Both measures serve to reduce production costs. However, by reducing the size, both efficiency and lifetime suffer.
Advantages Chip Scale LED
- Robust and durable
- Less expensive than conventional High Power LED
- Space saving installation
Disadvantages from Chip Scale LED
- Cost intensive
- Poor efficiency with white LED
- Little choice of colored LED
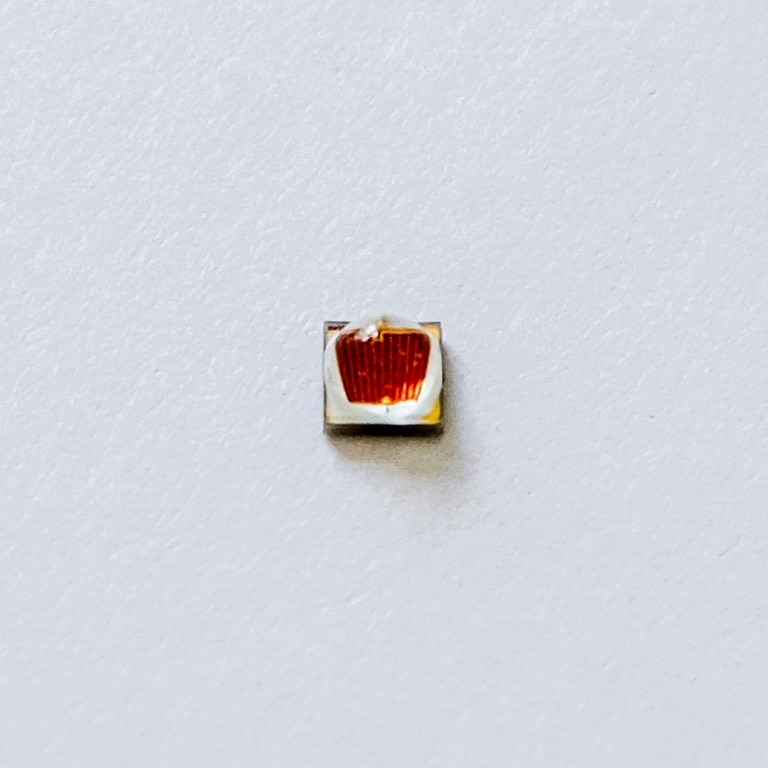

Mid Power LED
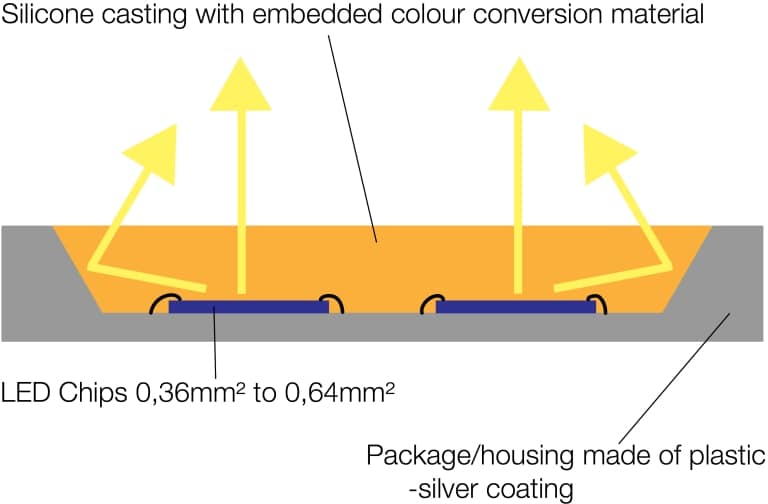
Mid Power LED are available in a wide range of price and performance classes. What they have in common is their construction from a plastic package and the embedding of the LED chip in silicone.
Structure
A mid-power LED basically consists of a plastic package. This package contains the LED chip, which is encapsulated in a mixture of silicone and color conversion material. The electrical contacting of the chip is realized via bondwires or flip chip technology.
Depending on the quality and (of course) the price, reflectors are integrated into the package. They should direct the light generated by the LED chip out of the package. The cheapest mid-power LED have no or insufficient reflectors and thus achieve only poor efficiencies.
With better mid-power LED, silver-coated or titanium oxide-coated reflectors are integrated into the package. The coating of the reflector has an influence on the performance and lifetime of the LED. Silver coated reflectors have the big disadvantage that they react with various chemicals and moisture. This leads to an oxidation of the reflector and thus to a reduction of the performance. One solution to prevent or slow down this oxidation is to apply a protective coating to the reflectors inside the LED. The most reliable way to maintain the performance of mid-power LEDs over the long term is to use titanium oxide as the reflector material. These LED have more than twice the lifetime (LM90).
LED with Titanium Oxide reflectors are currently only available from Samsung (LM301) or Seoul Semiconductor (3030-C12C). The use of these LED in combination with good encapsulation of the actual LED, are in our view the only solution to maintain the performance of the exposure system in the long term.
We would like to mention that the best midpower LED for horticulture applications are up to four times more expensive than low-cost LED. The performance of these LED lights differs only slightly at the beginning. However, after a few 1,000 hours of operation, the performance of low-cost LED decreases and thus noticeably reduces the yields. SANlight deliberately takes the sustainable long-life path with high-quality LED with titanium oxide reflector.
Chip on Board LED (COB)
Chip on board LED were commonly used in DIY luminaires a few years ago. Up to 100W of power can be achieved with a single LED. Such COB LED are still suitable for DIY projects where long life and best efficiencies are secondary.
Structure and Features
A highly reflective material (silver) is deposited on a ceramic or aluminum substrate. Then several chips connected in parallel and series are glued on and then encapsulated with a mixture of silicone and color conversion material. Such LED can be as large as 50mm x 50mm.
Even though COB are operated with low current, they hardly show the efficiency of modern mid power LED. More precisely, an imbalance in the performance/price ratio occurs. Similar to midpower LED, an aging issue arises due to oxidation of the reflector material. In addition, the chips become significantly hotter due to the high packing density. This also has a negative impact on the service life.
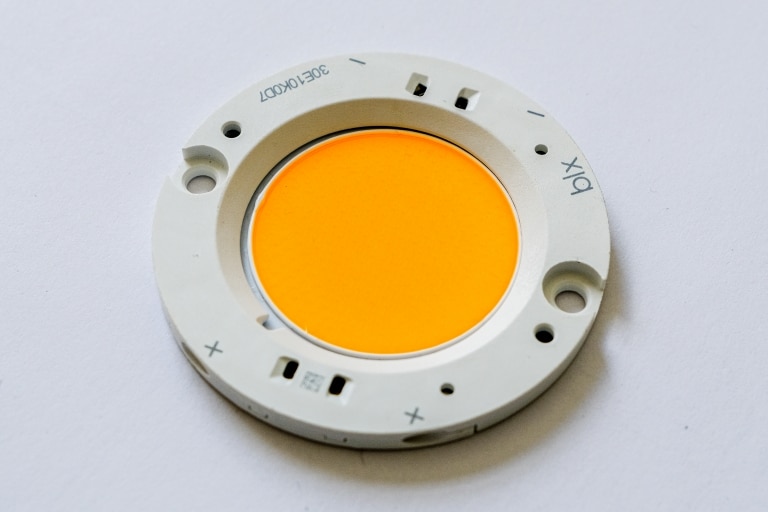

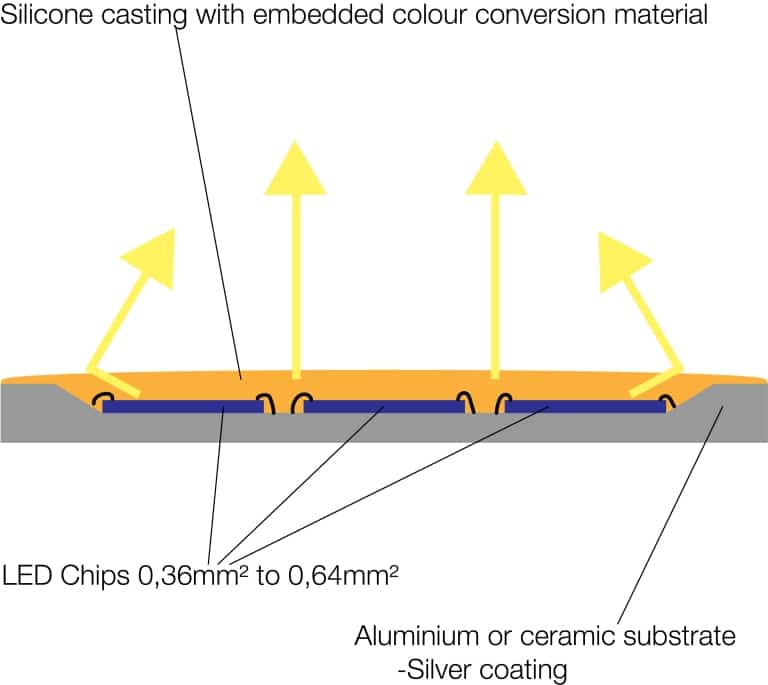
Chip Array LED (CA)
In addition to conventional LED technologies, there is a relatively new approach on the market with the Chip Array LED: A combination of Mid Power LED and COB LED.
Structure and features
Several chips are mounted in a plastic housing with an internal reflector. Also in these LED, the chips are then encapsulated with a mixture of silicone and color conversion material. Typical dimensions of such LED are 5mm x 5mm. If these LED are operated under their rated power, they are characterized by very good efficiency. Unfortunately, these LED types are still quite costly and their longevity has not yet been proven.